
Drivers, opportunities and obstacles for adopting Industry 4.0 in SME manufacturing sector
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) in Europe are facing rising pressures from the market and legislation to meet environmental standards. The Green Action Plan (GAP) is an EU initiative aiming at turning SME industry environmental challenges into business opportunities.
The GAP proposed addresses three issues: providing information and advice to SMEs on how to improve their resource efficiency in a cost-effective manner, supporting green technology transfer, and facilitating access to finance for environmental improvements. Thus, the links between the economy and the environment, in the SME industry, are high on the EU agenda. Digital technologies are seen as a promising tool for the transformation of SME manufacturing to a more sustainable one (European Parliament, 2015).
IDN releases a series of articles on digitalization as a driver for green growth in SME manufacturing. There will be four short articles with an overview of drivers for digitalization, opportunities for SME manufacturers in Industry 4.0 and obstacles for Industry 4.0 adoption in the SME industry sector.
Drivers for digitalization in SME manufacturing
It became challenging for the current economies to meet the continuously growing worldwide demand for consumer goods and capital and simultaneously ensure a sustainable evolvement of human existence in its economic, social and environmental dimensions. Recently, the creation of value in developed and developing countries is shaped by the rise of the fourth stage of industrialization (the so-called Industry 4.0), which means the adoption of digital technologies in the manufacturing sector (Stock & Seliger, 2016). For businesses facing the challenge of digital transformation, there are a number of drivers involved in decision-making processes, grouped in 5 main categories.
Internal drivers. The main drivers for firms, to invest in Industry 4.0 are internal, such as:

Picture. 1. Industry 4.0 and Sustainability. Source: European Union, 2018
- reducing production costs;
- improving the quality of products and services;
- improving employee productivity;
- production lead time reduction (European Commission, 2016).
Regulatory drivers. Sometimes regulatory interventions can play the role of a driver for digitalization. For example, the construction industry has been pushed down a compliance route by government procurement, introduced by some of the European countries, with the Netherlands as leader of best practices in that area. However, it needs to be emphasized that this kind of driver for adopting digital technology is rarely perceived as beneficial for individual firms, even if it is so (European Union, 2018).
Changing market needs. There is a growing demand for the personalization of mass-produced products, which is also called mass customization and can be achieved by automation. For example, certain furniture companies provide mass customization by offering multiple options for various components or features, such as different fabrics, furniture legs or pieces, which can be combined in numerous configurations.
Technology drivers. In the past decade, the cost of sensors, cloud infrastructure, bandwidth, and processing power has dropped significantly. Movement of the cutting-edge technologies into mainstream manufacturing makes the implementation of Industry 4.0 more applicable to the manufacturing industry. Affordable and easy to adopt technologies, without the requirement of great resources will be a crucial factor in the digital transformation of SMEs in Europe. Projects like Industry4SME or CM4Smart at IDN are bringing us closer to support this process.
Environmental drivers. Environmental activities, dealing with climate change, pollution and resource scarcity also play the role of a driver for digitalization. Companies that want to become more environmentally friendly start to implement Industry 4.0, because digital technologies lead to a more efficient allocation of resources, products, materials, energy, and water in the manufacturing industry, rise renewable energy use and decreased greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (European Union, 2018).
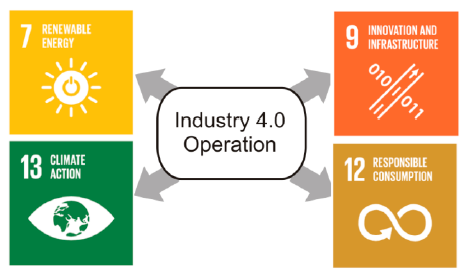
Picture. 2. Industry 4.0 and SDGs relations. Source: Bonilla et al., 2018
According to Riasat Noor (2019) there is a correlation between Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Industry 4.0. It is claimed that Industry 4.0 can contribute to sustainability and achievement of SDGs (especially Goal 7 “affordable and clean energy”, Goal 9 “industry, innovation and infrastructure”, Goal 12 “Responsible consumption and production” and Goal 13 “climate actions”) through promotion of sustainable industries, investment in research and development (R&D), motivation and opportunity for green entrepreneurship, application of software for energy optimization and adaptations in business processes, implementation of smart grids, implementation of life cycle assessments and integration with the circular economy (Bonilla et al., 2018; Noor, 2019).
All these drivers separately or in combination with each other can influence SME’s decision-making for the adoption of digital technologies in the industry sector.
Author: Yulia Marchuk



